|
|
|
Organization of Cells
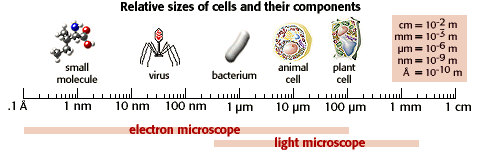
![]() The
Cell Theory
The
Cell Theory
The Cell Theory, proposed by three scientists in 1838, states that:
1. Cells are the basic units of structure and function
in living organisms
2. All living things are made of cells
3. Living cells come only from other living cells
Which three
scientists directly contributed evidence for the cell theory?
...search for the answer!!!
BIG
QUESTION: A key event in the origin of life was the formation of a
cell membrane. Why do you think this was so critical?
...click here for
the answer!!!
![]() Types
of Cells
Types
of Cells
There are two basic types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells...and here are their characteristics:
| Eukaryotes | Prokaryotes |
| Nucleus | No nucleus |
| Contain membrane-enclosed organelles | No membrane-enclosed organelles |
| Chromosomes in pairs | Single chromosome |
| Cell division by mitosis | Cell division without mitosis |
| Cellulose in cell walls | No cellulose in cell walls |
| DNA bound to histone proteins | No histone proteins |
| Kingdom Monera & Archaea | Kingdom Protista, Plantae, Fungae, & Animalia |
![]() A key feature
of eukaryotic cells is the structural division of the cell into smaller
functional parts called organelles . Compartmentalization
of cells increases functional efficiency by isolating specific processes and permitting a
division of labor within the cells.
A key feature
of eukaryotic cells is the structural division of the cell into smaller
functional parts called organelles . Compartmentalization
of cells increases functional efficiency by isolating specific processes and permitting a
division of labor within the cells.
Click on the following to view...
![]() Cells are compartmentalized into the following organelles:
Cells are compartmentalized into the following organelles:
Mitochondria - Mitochondria are referred to as the "powerhouse" of the cell because this is the site of ATP production in the cell. Mitochondria are enclosed in a double membrane, and they contain small amonts of DNA and RNA. They are surrounded by a double membrane with a series of folds called cristae.
Chloroplast - Chloroplasts are the compartment of photosythesis in plants and autotrophic protists. It is surrounded by a double membrane containing stacked thylakoid membranes in which light-absorbing pigments are embedded. The light absorbing pigments trap light energy to run the reactions of photosynthesis. The chloroplast, like the mitochondria, also contains its own DNA.
Plasma Membrane - The plasma membrane controls passage of materials into and out of the cell. It is composed of a combination of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates which provide this barrier, thus controlling transport and signalling systems.
Nucleus/ Nucleolus- The nucleus is the "control center" of the cell. This is where the DNA is kept and RNA is transcribed. RNA is transported out of the nucleus through the nuclear pores. Proteins needed inside the nucleus are transported in through the nuclear pores. There is a double membrane surrounding the nucleolus and the chromosomes. The nucleolus is the site of RNA synthesis and assembly.
Endoplasmic Reticulum - The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a tubular membrane system that compartmentalizes the cytosol. The Rough ER is covered with ribosomes, which are the site of protein synthesis. Rough ER is the site of sythesis, processing, and transport of proteins to the Golgi complex. Smooth ER is involved in the synthesis of steroids and metabolism of lipids.

Rough ER
Smooth ER
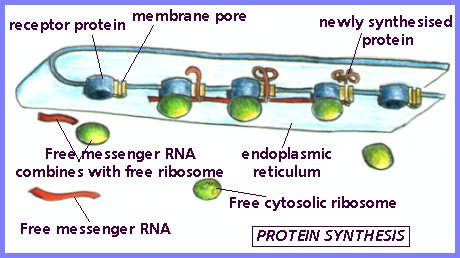
Golgi Apparatus - The Golgi apparatus is a series of stacked membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages macromolecules in vesicles for secretion or for delivery to other organelles.
Cell Wall - The cell wall is a rigid structure made of cellulose that surrounds and protects the plasma membrane of plant cells.Cell walls give shape and support to cells, and protect the content of the cells.
Click here for an electron micrograph of a plant cell, showing a cell wall
Click here for a plant cell diagram
Lysosome - The lysosome is the site of intracellular digestion, and is formed by budding from a Golgi apparatus. It is a special vesicle that contains enzymes for digesting and degrading old macromolecules for recycling of materials. Lysosomes are also capable of leaving the cell to destroy bacteria and foreign particles.
Vacuoles - Vacuoles are membrane-surrounded vesicles that contain water and storage materials in plants. They provide shape and support to cells, and aid in maintaining water balance in the cell and intracellular transport.
Major differences between plant & animal cells
Plant Cells Animal Cells Chloroplasts No chloroplasts Large Vacuoles Small Vacuoles Cell wall No cell wall Photosynthesize Do not Photosynthesize No Centrioles Centrioles
| General Biology | College Prep Biology | Honors Biology |
| Class Rules & Procedures | Science Links & Resources | Online Tools for Data Analysis |
| Search Engines | Parent's Page | Teacher Online Toolbox |